Why Is Silk So Expensive?
Silk has captivated the human imagination for thousands of years. Its shimmering surface, sensual feel, and ability to drape gracefully make it one of the most desirable fabrics ever created. From the emperors of China to the queens of Europe, silk has adorned the powerful and the fashionable, establishing itself as a universal symbol of elegance and luxury.
But despite the emergence of synthetic fibers and cheaper alternatives, silk remains expensive and coveted. Why? What is it about silk that justifies its premium price, even in today’s mass-produced textile industry?
This article explores the fascinating history of silk, the wide types of silk available today, the complex and labor-intensive process of silk production, how intricate techniques like silk printing add even more value, and finally, the many factors that contribute to its high cost.
By the end of this deep dive, you’ll understand why silk is not just a fabric — it’s a work of art, steeped in tradition and craftsmanship.
The Allure of Silk: A Historical Perspective
Silk’s story begins in ancient China around 2700 BCE. Legend tells of Empress Leizu, who discovered silk when a cocoon accidentally dropped into her tea. As she tried to remove it, the cocoon unraveled into a fine, gleaming thread that she soon learned could be spun and woven into a fabric unlike anything seen before.
This discovery revolutionized Chinese culture and industry. Silk was considered so precious that its production process was kept secret for centuries. Only royalty and high officials were allowed to wear it, and unauthorized silk trade or revealing of production methods was punishable by death.
Eventually, demand for this mysterious fabric grew so strong that the famous Silk Road was established — a vast trade network stretching from China to the Mediterranean. Caravans transported silk through deserts and mountains, exchanging it for gold, silver, spices, and other luxury goods.
Silk became a currency of power, diplomacy, and prestige. Even Roman emperors prized Chinese silk so highly they restricted its use to the aristocracy. That reputation for luxury has endured for over 5,000 years, adding to its high value even today.

Understanding the Types of Silk
One of the factors that contribute to silk’s cost is the wide variety of silk types, each with unique properties, rarity, and appeal. Not all silk is created equal — and understanding the types of silk helps explain why some are more expensive than others.
1. Mulberry Silk
By far the most common and expensive type of silk, mulberry silk is prized for its long, smooth fibers and unmatched softness. This silk comes from Bombyx mori silkworms fed exclusively on mulberry leaves. The uniformity and purity of the fiber result in a fabric with exceptional luster, strength, and feel.
Mulberry silk is used for premium bed linens, high-fashion garments, and fine accessories. Its durability and softness justify its higher price compared to other silks.
2. Tussar Silk
Tussar silk, or wild silk, is produced by silkworms that feed on oak and juniper leaves. This type of silk is more textured, has a natural golden hue, and feels less smooth than mulberry silk. Because the fibers are shorter and coarser, tussar silk is often less expensive — but still prized for its unique rustic appearance and natural charm.
3. Eri Silk
Sometimes called peace silk, eri silk is unique because it is harvested after the silkworm has left the cocoon, making it a cruelty-free alternative. Eri silk has a warm, wool-like texture and is less shiny than other silks. Its ethical production and sustainability make it more attractive to environmentally conscious consumers.
4. Muga Silk
Produced only in Assam, India, muga silk is famous for its natural golden color and incredible durability. Its rarity and the difficulty of production make it one of the most expensive silks in the world — often reserved for ceremonial garments and heirloom pieces.
5. Dupioni Silk
Dupioni silk is characterized by irregular slubs and a crisp texture, giving it a unique look and feel. It is often used in bridal and formal wear due to its ability to hold shape while providing a luxurious sheen.
Each type of silk serves a different purpose and appeals to different tastes and needs, creating a wide price spectrum.
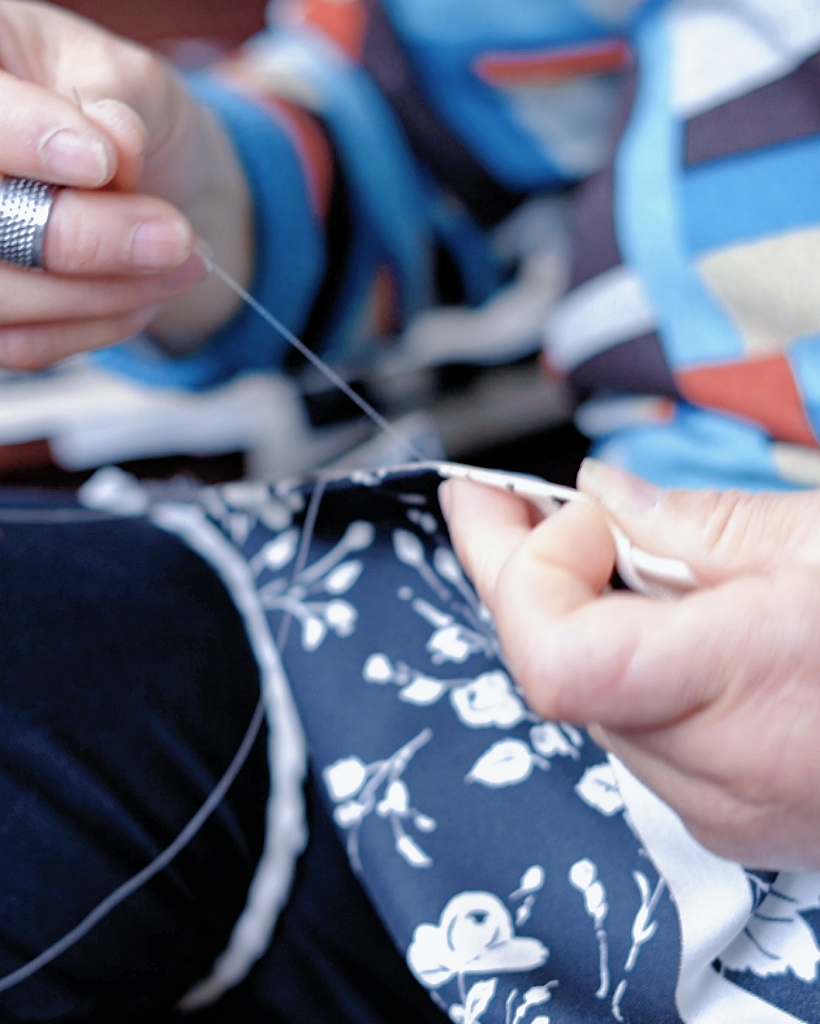
The Art of Silk Production
The most significant contributor to silk’s high cost is the painstaking and delicate process of producing it. From raising silkworms to weaving the final fabric, silk production is a masterclass in patience and precision.
1. Sericulture (Silkworm Farming)
Silk production begins with sericulture — the practice of raising silkworms in carefully controlled environments. Silkworms are sensitive creatures, requiring specific temperatures and humidity levels to thrive. Farmers must meticulously maintain these conditions, feeding the worms fresh mulberry leaves several times a day.
It takes around 2,500–3,000 cocoons to produce just one pound of raw silk. This high input-to-output ratio makes silk inherently costly.
2. Harvesting Cocoons
Timing is critical when harvesting. The cocoon must be collected before the moth emerges to avoid breaking the continuous filament. Workers must act quickly, often harvesting cocoons by hand to minimize damage.
3. Reeling the Silk
Next, the harvested cocoons are boiled to soften the sericin gum and kill the pupa inside. Then, each cocoon is carefully unwound to extract the single, long silk filament. Several filaments are combined into a thread strong enough for weaving.
This process, called reeling, requires skill and precision. Even a single misstep can result in uneven or broken threads, reducing quality.
4. Weaving and Finishing
Finally, the silk threads are spun into yarn and woven into fabric. Depending on the desired texture, sheen, and strength, different weaving techniques are employed. After weaving, the fabric may be dyed, treated, or printed to enhance its beauty and usability.
The entire process can take weeks or even months, and much of it still relies on skilled human hands.
Why Is Silk So Expensive? The Key Reasons
Given the effort and craftsmanship involved, silk’s high cost becomes understandable. But let’s break it down further into clear, specific reasons:
1. Labor-Intensive Process
From start to finish, silk production is highly manual. Even with modern machinery, many steps cannot be fully automated if quality is to be maintained.
2. High Resource Consumption
Raising silkworms requires vast amounts of mulberry leaves and water, making it resource-intensive compared to other fibers.
3. Delicate and Time-Consuming
Silk is fragile at every stage — from reeling to weaving — and takes time to produce even small amounts.
4. Vulnerability to Environmental Factors
Silkworms are highly sensitive to weather, temperature fluctuations, and disease. Entire crops can be lost to unfavorable conditions, increasing risk and cost.
5. Ethical and Sustainable Practices
As consumers demand more humane and eco-friendly practices, producers turn to peace silk and organic farming — both more expensive to implement.
6. Premium Finishing Techniques
Processes like silk printing, dyeing, and finishing are more challenging and costly than for other fabrics. Silk’s unique properties require specialized inks, dyes, and methods to avoid damage and preserve vibrancy.
7. Luxury Perception and Demand
Finally, silk’s centuries-old reputation as a luxury fabric ensures continued demand, especially in high-end fashion, bedding, and décor. The brand value of silk contributes to its price as much as its production cost.
The Role of Silk Printing in Value Addition
Silk printing — the process of applying patterns and designs onto silk fabric — adds not only aesthetic value but also monetary value to the material.
Printing on silk requires special expertise because the fabric’s smooth surface and delicate fibers make it prone to damage and ink bleed. Here are a few common techniques:
Screen Printing
Ideal for bold, vibrant patterns. Each color requires a separate screen, making it laborious but rewarding in quality.
Block Printing
A traditional, hand-crafted method where wooden blocks are used to stamp designs onto silk. It creates beautiful, artisanal fabrics, often seen in Indian and Southeast Asian textiles.
Digital Printing
Modern technology allows detailed, high-resolution images to be printed directly onto silk. Though faster, it still demands high-quality inks and careful handling.
These techniques add considerable labor and skill to the process — and justify higher prices for printed silk garments and fabrics.
Comparing Silk with Other Fabrics
To fully appreciate silk’s value, it helps to compare it with more common fabrics:
|
Fabric |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Silk |
Luxurious feel, natural sheen, breathable, hypoallergenic |
Expensive, requires special care |
|
Cotton |
Affordable, easy to wash, widely available |
Less lustrous, can shrink or wrinkle |
|
Polyester |
Cheap, durable, low maintenance |
Synthetic feel, not breathable |
|
Wool |
Warm, durable, natural |
Heavy, itchy, expensive |
Silk offers a unique combination of lightness, beauty, and natural luxury that other fabrics cannot replicate.
How to Identify Genuine Silk
Because of its high value, silk is often imitated. Here are tips to distinguish the real thing:
✅ Rub it — genuine silk feels warm and soft.
✅ Look for a subtle sheen — not the glossy shine of synthetic satin.
✅ Pull a thread and burn it — real silk burns slowly and smells like burnt hair.
✅ Observe irregularities — handwoven silk may have tiny imperfections, indicating authenticity.
Caring for Silk: Protecting Your Investment
Since silk is delicate, proper care is essential:
Always read care labels.
Dry cleaning is recommended for most silk garments.
If washing at home, use cold water and mild detergent.
Do not wring or twist — press gently to remove water.
Air dry away from direct sunlight.
Store in breathable bags with cedar or lavender to deter moths.
Caring for silk properly extends its life and preserves its beauty.

The Modern Appeal of Silk
Despite being an ancient fabric, silk remains relevant:
- In Fashion: From evening gowns to scarves, silk remains a favorite for designers worldwide.
- In Interiors: Silk curtains, cushions, and upholstery bring luxury into homes.
- Sustainability Trends: As a natural, biodegradable fiber, silk appeals to eco-conscious consumers.
- Ethical Choices: Peace silk and organic silk address modern concerns about sustainability and animal welfare.
Silk continues to evolve with modern tastes, combining tradition with innovation.
Conclusion: The True Cost of Luxury
So, why is silk so expensive?
Because it represents the pinnacle of nature’s artistry and human craftsmanship. Every step — from nurturing silkworms to weaving delicate threads, to adding intricate prints — demands time, skill, and care.
Owning silk means owning a piece of history, a fabric of unrivaled beauty, and a symbol of elegance that has endured for millennia.
When you choose silk, you choose more than just a fabric — you choose an experience of luxury that is worth every penny.
FAQs
What are the main types of silk?
The main types include mulberry silk, tussar silk, eri silk, muga silk, and dupioni silk, each offering different textures, sheen, and costs.
How is silk production different from other fabrics?
It requires raising live silkworms, manually reeling their delicate threads, and weaving them — a process far more laborious than producing synthetic fibers.
Why is silk printing more expensive than on other fabrics?
Printing on silk demands specialized techniques and handling to ensure colors remain vibrant without damaging the delicate fabric.
Are there affordable silk alternatives?
Yes — tussar or blended silks offer lower-cost options, though they lack the uniformity and softness of pure mulberry silk.
Can silk be produced sustainably?
Yes — peace silk and organic sericulture are gaining popularity for their ethical and environmentally friendly practices.
Ready to Start?
All of our printing services are operated professionally, and we control every part of the process from start to finish. Our professional team oversee everything from pre-treatment and printingthrcugh to finishing, qwality check and despatch, quaranteeing flawless results each and every time.